I’m solidly Gen X (who cares, whatever) and have for decades worked with various generations including some Silent Gens, many Boomers, scads of Millennials, and now, Gen Z.
A few years ago, I started to work with my first clients from Gen Z who were entering the workforce. And I must say that to my surprise, many of my Gen-Z clients expressed very different attitudes about their careers than their Millennial or even Gen-X counterparts.
The more I’ve worked with Gen-Z and observed the impact that their ideas and expectations are having on the world of work, the more I realized that this generation was shaking up business culture and work as we know it. So what are the changes that Gen-Z is expecting, or initiating, in the world of work? Here are a few major ways in which Gen-Z workers are changing the game. 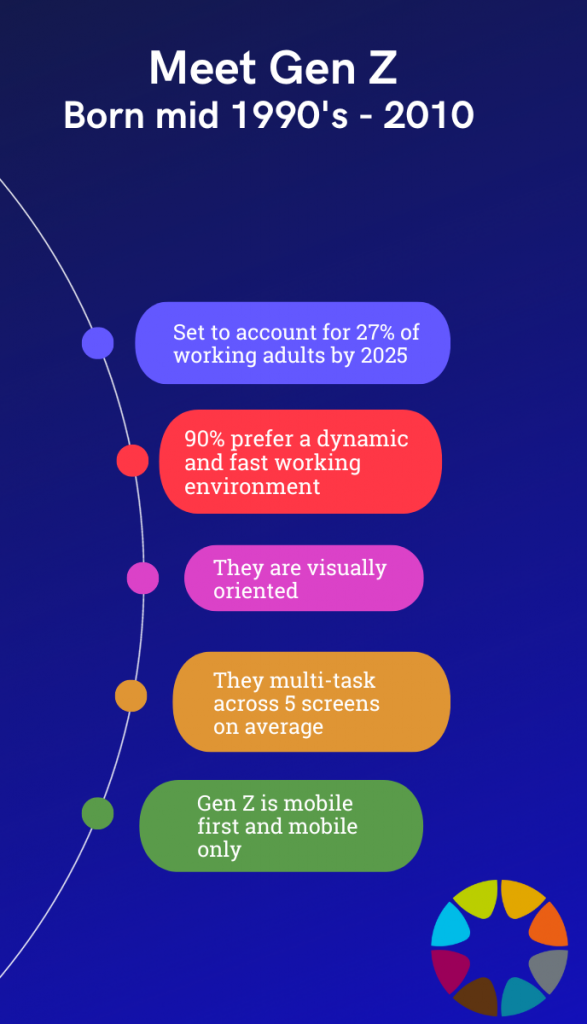
Technical Wizards. They’re beyond savvy. Gen Z grew up with screens and devices as pacifiers. Many of them write code and have their own monetized social channels. They can quickly adapt to new technology and may expect the workplace to provide them with up-to-date tools.
Because of this, they prefer digital communication: instant messaging, email, texts, and video conferencing. Face-to-face interactions may be less important to them than to previous generations.
We hear older generations say that these kids have no attention spans. This may be true, but they also use that to their advantage: they prefer clear, concise communication and they can efficiently multi-task between platforms, channels and various priorities.
Gen Z has grown up in a digital age with easy access to technology and the internet. This has given them the tools and resources to start businesses and market themselves online. Platforms like social media, e-commerce, and online marketplaces make it easier for them to launch entrepreneurial endeavors.
Entrepreneurial Spirits. Many Gen Z individuals have an entrepreneurial spirit. They value autonomy and may be interested in side hustles, freelance work, or opportunities to be highly creative and innovative in their roles. Why?
- Education: Entrepreneurship is often promoted in educational curricula and seen as a viable career path. Gen Z is exposed to entrepreneurship courses, programs, and events that encourage them to think creatively and take risks in the business world.
- Role Models: They have access to a wide range of young, successful entrepreneurs who have achieved fame and fortune through startups and online businesses. These role models can inspire Gen Z to pursue their entrepreneurial ambitions.
- Economic Uncertainty: Experiencing economic challenges and uncertainties, such as the 2008 financial crisis and the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, has made some Gen Z individuals more entrepreneurial as they seek financial stability and alternative income sources.
- Autonomy and Flexibility: Gen Z values autonomy and flexibility in their work. Entrepreneurship allows them to have more control over their schedules and work environments, aligning with their desire for work-life balance.
- Desire for Purpose: Many in Gen Z have a strong sense of social responsibility and a desire to make a positive impact on the world. Entrepreneurship can provide a platform to address social and environmental issues.
- Global Connectivity: The ability to connect with people worldwide through the Internet has opened up global markets and opportunities for Gen Z entrepreneurs. They can easily tap into international markets and collaborate with people from different cultures.
- Diverse Skill Sets: Gen Z is known for its diverse skill set and adaptability. They can combine various talents, such as tech-savviness, creative thinking, and communication skills, to launch and run businesses effectively.
- Networking and Crowdsourcing: Skilled at building online networks and communities. They can leverage these connections for advice, funding, and collaboration in their entrepreneurial endeavors.
This generation is the first generation to be able to grow up online. They have been introduced to a lot of problems and advantages. – Jaron Lanier
Socially Responsible, Diverse and Inclusive: Gen Z is known for its strong sense of social responsibility and environmental consciousness. They may seek out employers with a strong commitment to sustainability and corporate social responsibility. Global Perspective: Gen Z is likely to have a more global perspective due to their exposure to information and media from around the world. This can influence their attitudes toward international work and travel. This could all be due to:
- Information Access: Gen Z has grown up in an era of instant access to information through the internet and social media. This exposure has made them more aware of social, environmental, and political issues on a global scale.
- Globalization: Gen Z is a generation that is interconnected globally. They are exposed to news and information from around the world, which has made them more aware of international issues and interconnectedness.
- Environmental Concerns: Climate change and environmental issues have become prominent in public discourse during the formative years of Gen Z. They have witnessed the impact of environmental degradation and are concerned about the future of the planet.
- Activism and Movements: Gen Z has been influenced by and actively participated in various social and political movements, such as Black Lives Matter, climate strikes, and LGBTQ+ rights. These movements have highlighted the importance of social responsibility and activism.
- Social Media and Awareness: Social media platforms have given Gen Z a powerful voice to advocate for social issues. They use these platforms to share information, raise awareness, and mobilize support for causes they believe in.
- Parental Influence: Many Gen Z individuals have parents who also value social responsibility and activism. They’ve been raised in environments that encourage empathy, civic engagement, and social justice.
- Education and Curriculum: Schools and educational institutions have incorporated social responsibility and civic education into their curricula. Gen Z is taught about issues such as diversity, sustainability, and social justice.
- Access to Diverse Perspectives: Through the internet, Gen Z has access to a wide range of diverse perspectives and voices. This exposure can foster empathy and a sense of social responsibility as they learn about different cultures, backgrounds, and struggles.
- Economic and Political Uncertainty: Gen Z has experienced economic and political uncertainty, including the Great Recession and the COVID-19 pandemic. These challenges have made them more conscious of social and economic inequalities and the need for systemic change.
- Desire for Purpose: Gen Z often seeks meaningful work and a sense of purpose in their careers. They are more likely to choose employers and brands that align with their values and social responsibility principles.
- Peer Influence: Peer groups and social circles play a significant role in shaping the values and behaviors of Gen Z. Social responsibility can become a shared value among friends and peers.
- Technology and Innovation: Gen Z sees technology and innovation as tools to address social and environmental issues. They believe that technology can be harnessed for positive change.
What’s special about this generation is that they can see right through the facade and through the inauthenticity. – Shane Snow
Work-Life Balance: Achieving work-life balance is a priority for Gen Z. They may value flexible work arrangements, such as remote work or flexible hours, and place a premium on personal time. Some reasons:
- Technology and Connectivity: Gen Z has grown up in a highly connected digital world. While this connectivity offers many benefits, it also means that work can encroach on personal time more easily. To maintain a healthy balance, they seek clear boundaries between work and personal life.
- Mental Health Awareness: Gen Z is more attuned to mental health issues and the importance of managing stress and burnout. They recognize the adverse effects of overworking and prioritize their well-being.
- Witnessing Burnout: Many in Gen Z have observed older generations, particularly millennials, experiencing burnout and dissatisfaction with work-life balance. This has motivated them to prioritize balance in their own lives.
- Desire for Leisure and Personal Growth: Gen Z values leisure time for personal growth, hobbies, and spending time with loved ones. They see work-life balance as a means to achieve a well-rounded and fulfilling life.
- Flexibility and Autonomy: Gen Z appreciates flexibility and autonomy in the workplace. They want the freedom to manage their work schedules to accommodate personal commitments and interests.
The above characteristics are the primary things to think about when hiring and retaining Gen Z talent. There are a few more aspects to keep in mind as well.
Continuous Learning: They are motivated to continually learn and develop new skills. They may prefer workplaces that offer opportunities for professional growth and development.
Instant Gratification: Accustomed to quick access to information and services, which can make them expect prompt feedback and results in their work.
Pragmatic and Realistic: This generation is often considered practical and realistic. They may be more risk-averse in their career choices and seek job security.
Competitive: Competitive not only in terms of wanting to advance in their careers but also in seeking recognition and validation for their achievements.
I think that trying to evaluate the behavior of an entire generation can be tricky, especially one this young. Of course, everyone is an individual, and no one wants to be lumped in with millions of their peers purely based on the year they were born.
Nevertheless, I think that the research and data show that Gen Z workers are bringing some fresh ideas and a strong work ethic to the world of work. I’m so excited to watch as things change for the better to catch up with their forward-thinking perspective.

